FUE does not leave behind a linear scar in the donor area, making it suitable for patients who prefer keeping their hair short or have issues such as scalp laxity making traditional strip extraction unsuitable.
At a FUE hair transplant, surgeons will create small puncture marks in your scalp where follicular units will be harvested – these will leave small dot-shaped scars.
Donor Area
An integral component of hair restoration surgery involves harvesting donor follicles from the back and sides of the scalp – usually where there is less likelihood of balding – for transplant. Hair here typically resists thinning over time, making this an excellent source for harvesting enough grafts for successful transplant.
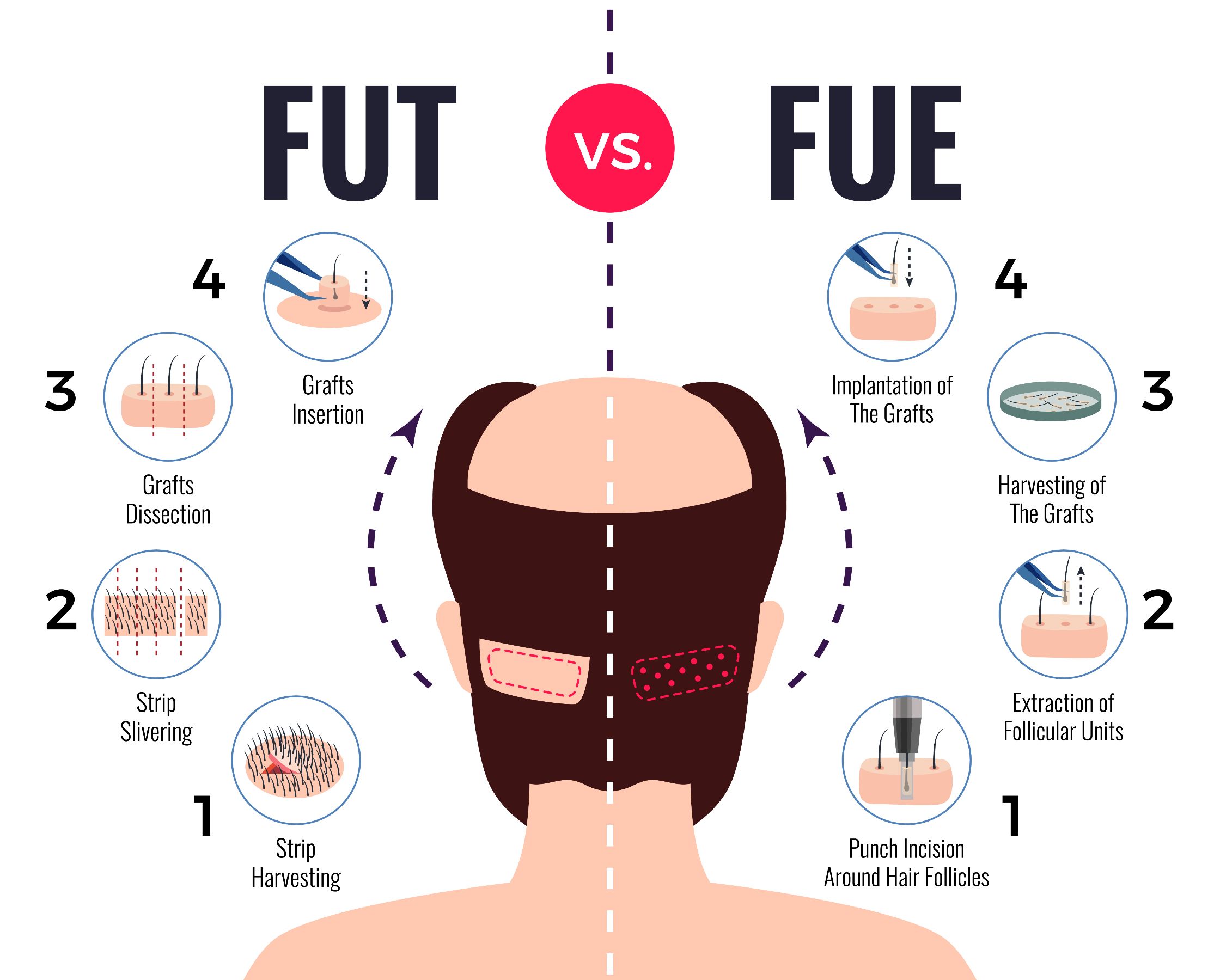
Follicular Unit Transplantation, or FUT, involves surgically extracting a thin strip of hair-bearing skin from the donor region and closing this wound, leaving behind one generally fine linear scar. Modern techniques and instrumentation use minimal transection during FUT procedures, thus lowering risk of visible scarring post surgery.
FUT surgery scars are typically concealed by surrounding hair; however, short haircuts may make the scar more obvious. Luckily, several techniques exist that can be employed to lessen its appearance such as tumescent anesthesia, undermining, absorbable sutures, buried sutures and trichophytic closure.
Follicular Unit Excision, or FUE, involves manually extracting individual hair follicles from donor regions using punch tools, creating small dot-like scars in the scalp that may become visible with short haircuts. Furthermore, these scars may distort nearby follicular units thereby decreasing donor supply; however, FUE is typically painless and takes less time than FUT to complete.
Extraction
FUE harvests individual hair follicles from the sides and back of your scalp in order to transplant them in areas suffering from hair loss. Follicles from these locations tend to be DHT resistant and less vulnerable to androgen hormones which contribute to male pattern hair loss.
Fue transplants differ from strip techniques in that they leave no linear scar. Instead, this procedure utilizes small puncture marks which heal within days and can easily be concealed by long hair in nearby areas.
FUE is ideal for patients looking for quick results and wish to resume a normal lifestyle quickly; however, this technique may be less suitable if larger numbers of grafts are necessary and more costly than the strip method.
Although modern techniques and instrumentation significantly decrease transection and damage to hair follicles during extraction, there still exists the risk of injury to some percentage of grafts that must be harvested, which affects final results and could limit total harvest numbers.
ARTAS robotic system was specifically created to harvest more follicles while leaving minimal or no scarring, and is much safer and preciser than other methods. Furthermore, its harvesting method produces more natural-looking transplants as follicles are taken from all over your head and body rather than just from one narrow strip in your donor area.
Transplantation
FUT involves taking a strip of skin from your scalp and extracting it to harvest grafts that produce DHT resistant hair, transplanting these to areas with bald spots. Grafts will usually come from mid-portions of permanent zones as these produce stronger and less susceptible to future thinning or going balding.
This type of hair restoration procedure is best suited to men suffering from androgenic alopecia in the Norwood pattern, such as those experiencing receding hairlines or Ludwig patterns. Furthermore, this will not work if you suffer from medical conditions like thyroid disorder or alopecia areata.
FUT requires more donor area, which may result in scarring. Furthermore, surgery may take longer. But the good news is that any scarred areas will fade with time as it heals; long hairstyles will help conceal it further.
FUE is an effective solution for hiding scars from previous surgeries, and is particularly appealing for women looking for non-invasive ways of covering up stitches with bandages or shaving their heads. Furthermore, unlike FUT which leaves a linear scar behind it can even help disguise any visible FUT scars in donor areas.
Recovery
One of the primary concerns when considering hair transplant is scarring. FUT falls short in this respect as it leaves an obvious strip-like scar on your scalp which doesn’t look very nice; while FUE leaves small micro scars which are barely detectable by anyone who doesn’t know you personally.
Based on your specific hair graft needs, both procedures should take approximately equal time to complete. FUT tends to be slightly more invasive as it involves extracting hair follicles as a strip rather than individual grafts – thus increasing discomfort as well as lengthening recovery time.
After surgery, your scalp will likely experience some scabbing that typically lasts from two to six days after treatment. It is important not to touch this area during this time as touching can damage new grafts which then won’t grow and could leave some scars behind which eventually come off on their own – no cause for alarm here!
After the scabs have dissipated, new hair growth should become visible in your transplanted areas. At first it may have a baby-fine texture; over time however it should thicken gradually until its full growth occurs about one year post operation.
Disclaimer: The content on this blog is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for personalized advice. Information regarding plastic surgery, dental treatment, hair transplant, and other medical procedures is educational and not a guarantee of results. We do not assume liability for actions taken based on blog content. Medical knowledge evolves; verify information and consult professionals. External links do not imply endorsement. By using this blog, you agree to these terms.