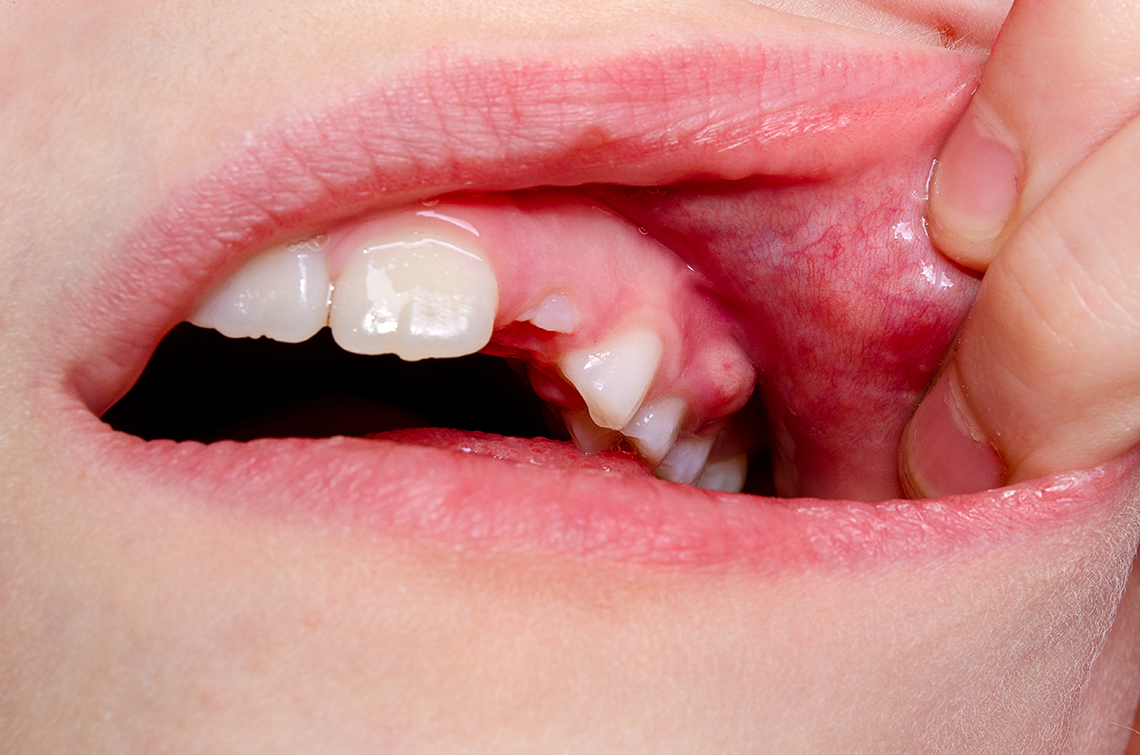
A pus tooth is caused by a bacterial infection in the pulp of a tooth and can result in foul-smelling material (pus), pain and swelling in that area of a mouth. The infection results in foul smells, discomfort and swelling.
The periosteum provides support to bones during infancy. Additionally, it enhances their development after fracture or injury by stimulating repair mechanisms within it.
Causes
A pus tooth is a pocket of pus that forms within a tooth or gum due to bacterial infection, and will not go away on its own. Treatment must be sought immediately as symptoms may include pain, swelling, bad taste in mouth/jaw and food sensitivities. If left untreated for too long it could spread further resulting in sepsis which could even lead to death if not addressed immediately.
Pustules in teeth may be caused by several different causes, including dental abscess or gum boil. Tooth decay is another potential source, by creating holes in its hard outer layer (enamel) through which bacteria infiltrate the pulp area – an infection often spreading into bone that supports and surrounds a tooth as it spreads causing periodontal abscess or gingival abscess respectively.
Periapical abscesses are among the most dangerous types of pus tooth infections, as bacteria reach out from beneath a tooth’s root tip to cause a painful swelling in the jaw and cause inflammation and an abscess to form at its tip. A periapical abscess may also damage adjacent teeth resulting in widespread dental infection.
If left untreated, pus tooth bacteria can quickly escalate to cause septicemia or sepsis – an infectious illness which can lead to shock and respiratory failure, potentially entering the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body – potentially including even reaching critical organs like the brain for which medical assistance would likely be required in an emergency situation.
Pus tooth can be treated by draining an abscess or performing a root canal procedure. Your dentist will make a small cut in the abscess to drain it and clean out its contents using saline solution, before cleaning and sealing its pulp chamber, extracting infected roots, and covering them with crowns to prevent future reinfection. In extreme cases, they might remove and replace it entirely with another tooth.
Symptoms
When bacteria invade a broken, chipped, or decaying tooth they cause an infection which swells surrounding tissues, leading to a painful toothache and spreading into gums and jawbone. If it goes untreated quickly a pus pocket called dental abscess may form and lead to additional health concerns including septic shock.
Pustooth symptoms include pain and an unpleasant taste in the mouth, swelling of the face and jawbone, difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing, fever and an abscess rupture that releases foul-tasting or salty fluid from your mouth and into your throat. Once an abscess breaks open it’s a medical emergency and individuals should seek professional assistance immediately.
If you suspect an abscess is developing in your mouth, visiting a dentist is the only sure way to diagnose and prescribe antibiotics; but in the interim there may be home remedies you can try that can reduce pain while controlling infection until an appointment with the dentist can be scheduled.
Rinsing your mouth with warm salt water is an effective way to disinfect an infected area and clear away bacteria. Combine 1/2 teaspoon of table salt with warm water and swish in your mouth for at least 1 minute, before spitting out and repeating several times each day until seeing your dentist.
Over-the-counter painkillers may help relieve discomfort caused by pus-filled teeth. Ibuprofen may be appropriate, though aspirin should also be taken according to package directions. These medications should not be given to children under 16.
If you can’t reach a dentist immediately, visit your local emergency department or family doctor for advice. They may be able to suggest self-care steps and ways of alleviating symptoms until you can see a dentist. If an abscess opens up and causes septic shock, hospital admission may be required; pus tooth infections can be extremely dangerous and untreated could worsen rapidly; symptoms include severe pain, fever and swollen gums – the latter often closing off airways – potentially life threatening complications can ensue if left untreated – they must be addressed as quickly as possible or hospital admission will ensue.
Treatment
Pus that collects in the root of a tooth indicates infection. Unlike pimples, pus from tooth infections is thick and yellow in color and contains living bacteria as well as white blood cells and dead tissue. Left untreated, an untreated pus tooth infection could spread into its surroundings including bone, gums, tissue and even enter your bloodstream, leading to life-threatening septicemia infections that require hospitalization for treatment.
Dental abscesses can be painful but treatable. The goal of treatment should be to clear away infection and save the tooth. Pus is produced when our immune systems cannot cope with all the bacteria residing within a tooth and the pressure it puts on its nerves, leading to infection or inflammation forming inside it.
Treatment options for pus tooth include root canal, incision and drainage or extraction of the infected tooth. With incision and drainage, a cut is made into the abscessed area in order to drain out pus from inside it; this can be performed by either a dentist or endodontist – who may also insert a small rubber drain to keep draining as they drain it out.
An incision and drainage procedure is often the best way to drain a pus tooth. A dentist or endodontist will make a small cut in your gums before using salt water to rinse out. A small rubber drain will then be placed into your abscess until all the pus has drained from it.
Good oral hygiene habits can help treat infections of the tooth and gums with regular brushing, flossing, and visits to a dentist or dental hygienist for professional cleanings. Flossing helps remove plaque and food debris between the teeth to help prevent decay; flossing can also remove food debris that gets caught between them during brushing sessions. In order to protect their teeth and gums more effectively it’s wise to limit consumption of sugary foods/beverages/beverages/mouthguards worn by athletes, use fluoride toothpaste and rinse warm saltwater after brushing/rinsing routinely rinsing can help keep everything clean!
Symptoms of mouth pain include swelling of jaw or gums, bad breath, pus formation and/or fever. Untreated infections can lead to serious health concerns like sinusitis, periapical abscess, bone and tissue damage as well as septicemia if left untreated.
Prevention
Abscessed teeth can be excruciatingly painful. Causes may include untreated dental decay or broken or chipped teeth that allow bacteria to seep in. Left untreated, an abscessed tooth infection could spread from its origin in your jaw to other areas of your head or neck – the best way to avoid such problems is with proper dental hygiene – brushing, flossing and using mouth rinses regularly as part of an overall dental plan.
Root canal therapy can also play a vital role in maintaining your dental health. A root canal procedure allows dentists to remove infected nerves, veins and arteries from within a tooth’s root structure and allow it to heal properly; the procedure can be performed by either an endodontist (specialist who treats damaged or infected teeth) or dentists themselves.
When pus can’t drain from an infected site, it can accumulate and build pressure that puts pressure on blood vessels, possibly rupture them and lead to sepsis, an incurable life-threatening condition which affects organs throughout your body. For your own health’s sake and the wellbeing of others, see your physician as soon as you notice a pus-filled pocket in order to seek immediate medical advice.
Garlic is an effective natural antibiotic that can treat infections in multiple parts of your body, including gums and mouth. Allicin, found in garlic cloves, has been demonstrated to kill bacteria during lab studies; you can eat it or apply a paste made of crushed cloves several times each day directly onto the infection site for relief.
Salt is another pantry essential that boasts antibacterial properties. When mixed with warm water, it can be used to rinse away bacteria in your mouth or around a tooth infection. Rinsing with salt water reduces bacteria while helping clear away debris from your oral cavities and breaking up pus build-up so the infected area heals faster.
An effective treatment for tooth infection can also include using a 35% hydrogen peroxide solution. Gently swirl this solution around in your mouth for approximately one minute before spitting out and repeat as necessary. Be wary not to swallow the solution, as hydrogen peroxide can damage both tooth enamel and gum tissue.
Disclaimer: The content on this blog is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for personalized advice. Information regarding plastic surgery, dental treatment, hair transplant, and other medical procedures is educational and not a guarantee of results. We do not assume liability for actions taken based on blog content. Medical knowledge evolves; verify information and consult professionals. External links do not imply endorsement. By using this blog, you agree to these terms.